IFrame Detection
Attackers can inject a hidden iframe into a webpage and steal the user’s session (cookie). This attack is similar to a redirect, however by leveraging the iframe technique, attackers can perform illicit behavior behind the scenes and avoid the detection of having visited a malicious website.
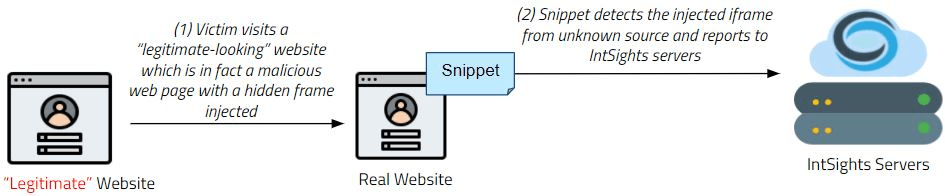
The following steps illustrate how the Phishing Watch works when an iframe is used:
- The Phishing Watch JavaScript snippet is created and embedded in the website.
- The snippet launches each time the webpage is loaded or refreshed.
- When the snippet identifies a nonformal suspicious website (by inspecting the URL of the webpage), it reports the suspicious URL back to Digital Risk Protection (Threat Command) servers in a stealthy, low footprint manner.
- The Digital Risk Protection (Threat Command) phishing detection algorithm determines whether the reported website could be used for phishing.
- The snippet’s allowlist excludes cases where it may be operating on the organization’s official website.